Printable List of Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, a condition characterized by inflamed pouches in the colon, can be effectively managed through dietary modifications. Understanding the foods to avoid and their alternatives is crucial for individuals seeking relief from symptoms and preventing future flare-ups.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed list of foods to avoid, organized into categories, along with their potential impact on diverticulitis. It also offers healthy alternatives and dietary recommendations tailored to individuals with this condition.
Introduction

Diverticulitis is a condition that affects the large intestine. It occurs when small pouches called diverticula become inflamed or infected. Diverticula are small, bulging sacs that can form in the walls of the large intestine.
Diverticulitis can be a painful condition that can lead to a number of complications, including bleeding, perforation, and abscess formation. In severe cases, it can even be fatal.
There is no cure for diverticulitis, but it can be managed with a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. One of the most important lifestyle changes that people with diverticulitis can make is to follow a healthy diet.
Dietary Modifications for Diverticulitis
A healthy diet for diverticulitis includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are high in fiber, which can help to keep the stools soft and easy to pass. Fiber can also help to reduce the pressure in the large intestine, which can help to prevent diverticula from forming.
In addition to eating a high-fiber diet, people with diverticulitis should also avoid foods that are high in fat and cholesterol. These foods can contribute to the formation of diverticula.
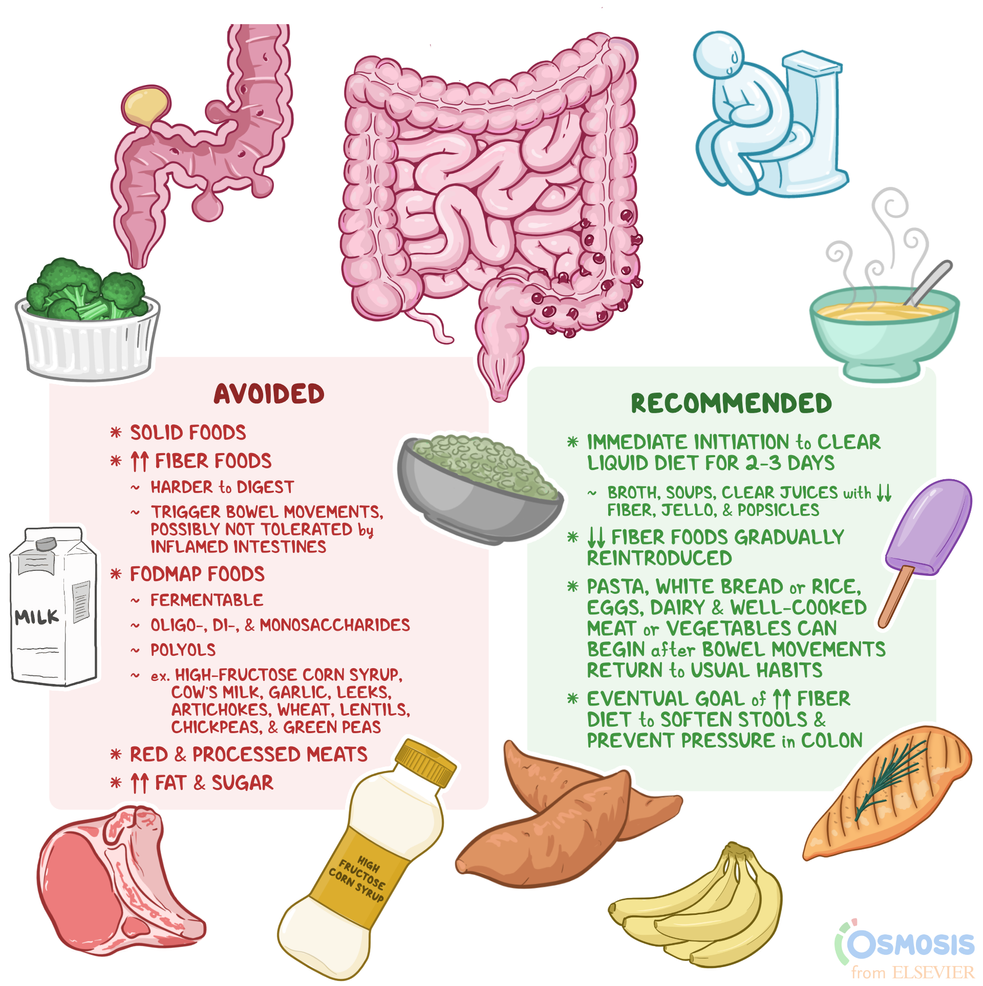
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition that causes inflammation and infection in the small pouches (diverticula) that can form in the lining of your colon. Certain foods can aggravate diverticulitis and make symptoms worse.
Here’s a comprehensive list of foods to avoid if you have diverticulitis:
Fruits
- Seeds: Avoid fruits with small, hard seeds, such as strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries. Seeds can get stuck in diverticula and cause inflammation.
- Citrus fruits: Limit citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons. They contain citric acid, which can irritate the colon.
Vegetables
- Cruciferous vegetables: Avoid cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. They contain compounds that can produce gas and worsen diverticulitis symptoms.
- Corn: Corn kernels can get trapped in diverticula and cause irritation.
- Nuts and seeds: Avoid nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds. They can be difficult to digest and can get stuck in diverticula.
Meats
- Tough meats: Avoid tough meats like steak and pork chops. They are difficult to digest and can cause inflammation.
- Processed meats: Limit processed meats like bacon, sausage, and hot dogs. They contain high levels of saturated fat and sodium, which can worsen diverticulitis.
Dairy
- Dairy products: Limit dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt. They can cause gas and bloating, which can aggravate diverticulitis.
Processed Foods
- Refined grains: Avoid refined grains like white bread, pasta, and rice. They are low in fiber and can contribute to constipation, which can worsen diverticulitis.
- Sugary foods: Limit sugary foods like candy, soda, and desserts. They can cause inflammation and worsen diverticulitis symptoms.
Alternatives to Avoided Foods
Avoiding certain foods can be challenging, especially if you’re not sure what to eat instead. Here are some healthy alternatives to the foods you should avoid with diverticulitis, along with the key nutrients they provide.
By incorporating these alternatives into your diet, you can ensure that you’re getting the nutrients you need without compromising your health.
Grains
- Avoid: Whole wheat bread, brown rice, whole wheat pasta
- Alternatives: White bread, white rice, refined pasta
- Key nutrients: Carbohydrates, energy
Fruits
- Avoid: Raw apples, pears, berries
- Alternatives: Bananas, melon, canned fruit
- Key nutrients: Vitamins, minerals, fiber
Vegetables
- Avoid: Raw vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, corn
- Alternatives: Cooked vegetables, such as carrots, potatoes, green beans
- Key nutrients: Vitamins, minerals, fiber
Nuts and Seeds
- Avoid: Nuts and seeds with hulls, such as almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds
- Alternatives: Nut butters, seed butters, hulled nuts and seeds
- Key nutrients: Protein, healthy fats, fiber
Other
- Avoid: Popcorn, dried fruit
- Alternatives: Air-popped popcorn, fresh fruit
- Key nutrients: Fiber, antioxidants
Dietary Recommendations

Listen up, peeps with diverticulitis. Grubbing on the right stuff can make a massive difference in keeping those pesky symptoms at bay. Here’s the lowdown on what to chow down on and what to steer clear of.
First off, it’s all about fiber. This magic ingredient keeps your bowels moving smoothly, which is crucial for preventing flare-ups. Aim for around 25 grams of fiber a day. You can get your fix from fruits, veggies, and whole grains.
Fiber-Rich Foods
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, oranges
- Veggies: Broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, spinach
- Whole grains: Brown rice, oatmeal, quinoa
Another key player is fluids. Staying hydrated helps soften your stools and makes them easier to pass. Aim for eight glasses of water a day, or more if you’re sweating it out.
Tips for Adding Fiber
- Start slow: Gradually increase your fiber intake to avoid bloating and gas.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Water helps your body absorb fiber more easily.
- Choose soluble fiber: This type of fiber dissolves in water and can help soften stools.
Other Considerations

Dietary Factors: FODMAPs and Probiotics
Dietary factors beyond the specific foods to avoid may also influence diverticulitis. One area of interest is the role of fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs). These are short-chain carbohydrates that can trigger digestive symptoms in some people, including those with diverticulitis. Limiting FODMAP intake may help reduce symptoms.
Probiotics, live microorganisms that offer health benefits, may also play a role in managing diverticulitis. They can help balance the gut microbiome, which may reduce inflammation and improve digestive function.
Stress and Lifestyle
Stress and lifestyle factors can also impact diverticulitis. Chronic stress can worsen symptoms, as it can lead to changes in gut motility and immune function. Regular exercise, stress-reducing techniques, and adequate sleep can help manage stress and improve overall health.
Resources for Further Information and Support
- Diverticular Disease Health Center: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/diverticular-disease
- American Gastroenterological Association: https://www.gastro.org/patient-care/conditions/diverticular-disease
- International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: https://iffgd.org/gi-disorders/diverticular-disease/
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important dietary recommendation for diverticulitis?
Maintaining a high-fiber diet is essential for preventing and managing diverticulitis. Fiber promotes regular bowel movements, reducing pressure on the colon and preventing the formation of diverticula.
Can I eat nuts and seeds with diverticulitis?
Nuts and seeds are generally not recommended for individuals with diverticulitis due to their potential to lodge in diverticula and cause inflammation. However, some nuts, such as almonds and walnuts, can be consumed in moderation if ground or chopped.
Is dairy harmful for diverticulitis?
Dairy products are not typically restricted in a diverticulitis diet. However, some individuals may experience increased symptoms after consuming dairy, so it is recommended to monitor your response and adjust your intake accordingly.