The Ultimate Guide to Printable Form 1040 Sr: Simplifying Taxes for Seniors
Filing taxes can be a daunting task, especially for senior citizens. However, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has created a simplified tax form specifically designed to meet the needs of seniors: Form 1040-SR. This user-friendly form streamlines the tax filing process, making it easier for seniors to fulfill their tax obligations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Form 1040-SR, providing a step-by-step walkthrough, addressing common pitfalls, and highlighting special considerations for seniors. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and resources to navigate the tax filing process with confidence.
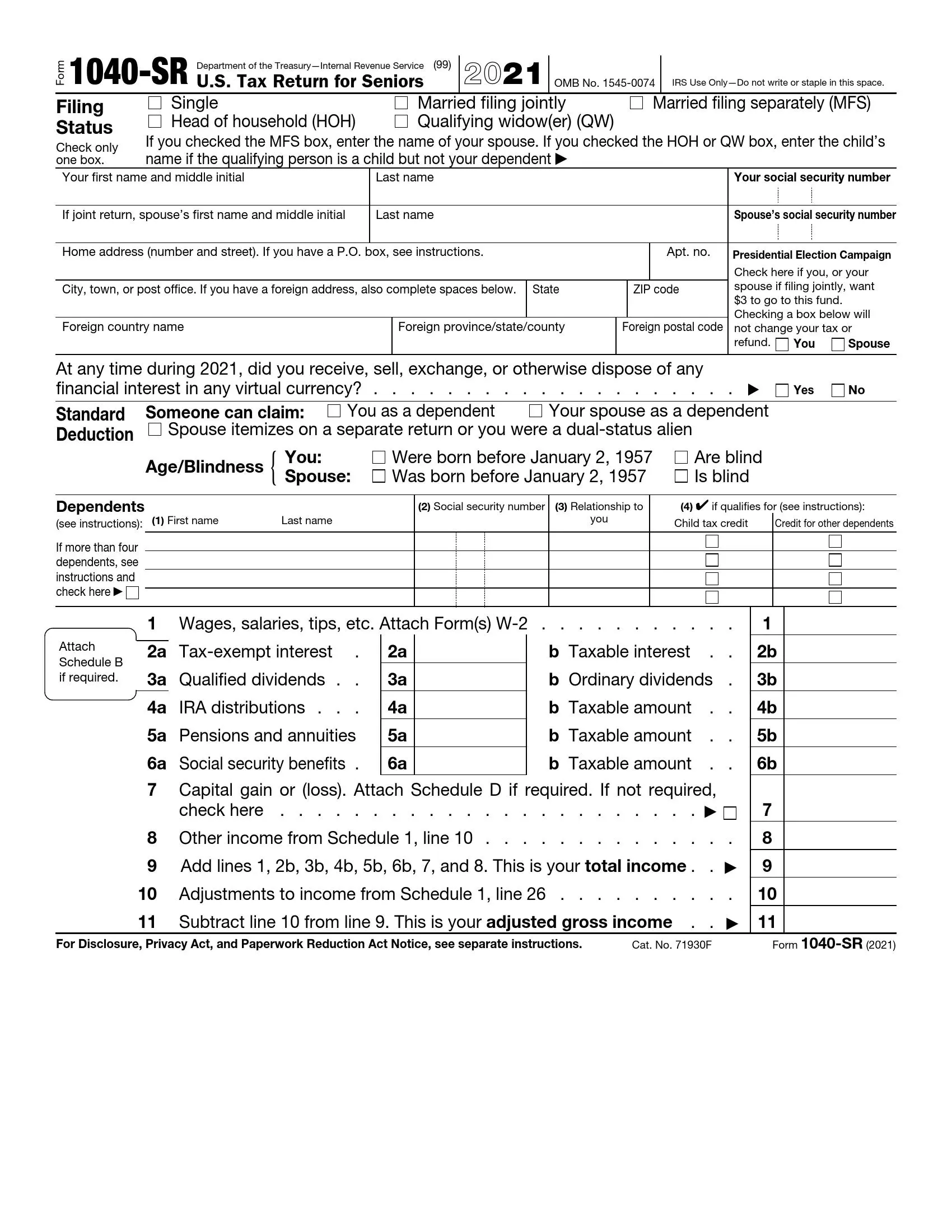
Overview of Form 1040-SR
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1040-SR-TaxReturnforSeniors-1-ccfefd6fef7b4798a50037db30a91193.png?w=700)
Blud, if you’re a proper geezer or bird who’s minted, then Form 1040-SR is your ticket to sorting out your taxes, innit? It’s like a cheat code for tax time, mate.
Back in the day, when taxes were a right pain in the backside, the taxman came up with Form 1040-SR to make life easier for us lot. It’s like a simplified version of the regular 1040 form, but with all the bells and whistles you need to get your tax sorted without any hassle.
Benefits of Using Form 1040-SR
- It’s a doddle to fill in, even if you’re not the sharpest tool in the shed.
- You can use it to claim all the tax breaks you’re entitled to, so you don’t have to fork out more dough than you should.
- It’s the perfect choice if you’re a young gun or a pensioner who doesn’t have any complicated tax affairs.
s for Completing Form 1040-SR

Filling out Form 1040-SR is easy if you have the right s and guidance. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you complete the form accurately and efficiently.
Personal Information
Start by filling out your personal information, including your name, address, Social Security number, and filing status. Ensure the information you provide matches your official records to avoid any delays or errors in processing your return.
Income
Next, report your income from various sources, such as wages, salaries, dividends, and interest. Use the appropriate schedules to report specific types of income, such as Schedule B for interest and dividends.
Adjustments to Income
In this section, you can deduct certain expenses from your income to reduce your taxable income. Common adjustments include contributions to traditional IRAs, student loan interest, and alimony paid.
Itemized Deductions vs. Standard Deduction
Choose between itemizing your deductions or taking the standard deduction. Itemizing allows you to deduct specific expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable contributions. The standard deduction is a fixed amount that varies depending on your filing status.
Taxable Income
Subtract your adjustments and deductions from your income to calculate your taxable income. This is the amount of income subject to taxation.
Tax Calculation
Use the tax tables or tax software to calculate your tax liability based on your taxable income and filing status. The tax tables provide tax rates for different income ranges.
Credits
Claim any applicable tax credits to reduce your tax liability further. Common credits include the child tax credit, earned income credit, and retirement savings contributions credit.
Payments and Refund
Report any estimated tax payments, withholding taxes, or other payments you’ve made towards your taxes. If your payments exceed your tax liability, you’ll receive a refund. If you owe taxes, you’ll need to make a payment with your return.
Common Errors and Pitfalls

Filling out Form 1040-SR can be a bit of a minefield, and it’s easy to make mistakes that could cost you money or even lead to penalties. Here are some of the most common errors to watch out for:
Not checking the accuracy of your information. Make sure all the information you enter on your tax return is correct, including your Social Security number, address, and income. Even a small error can cause your return to be delayed or rejected.
Entering the wrong filing status
Your filing status determines how your income is taxed. If you choose the wrong filing status, you could end up paying more taxes than you should. Make sure you understand the different filing statuses and choose the one that applies to you.
Not claiming all of your deductions and credits
Deductions and credits can reduce your taxable income, which can save you money on taxes. Make sure you claim all the deductions and credits you’re eligible for. However, don’t make up deductions or credits, as this could lead to an audit.
Making math errors
Math errors are one of the most common mistakes people make on their tax returns. Double-check your math before you submit your return to avoid any costly mistakes.
Filing late
Filing your tax return late can result in penalties and interest charges. File your return on time, even if you can’t pay the taxes you owe. You can request an extension if you need more time to file.
Special Considerations for Seniors
Form 1040-SR includes special considerations and adjustments tailored to the unique financial situations of senior citizens. These considerations aim to provide tax relief and support to elderly taxpayers.
To be eligible for these special considerations, individuals must meet specific age and income requirements. Generally, taxpayers must be age 65 or older by the end of the tax year and have a gross income below certain thresholds.
Standard Deduction
Senior citizens receive a higher standard deduction than younger taxpayers. This deduction is a set amount that reduces the amount of taxable income, effectively lowering the tax liability.
For 2023, the standard deduction for seniors is:
- Single: $15,800
- Married filing jointly: $27,700
Additional Deductions
Seniors may also qualify for additional deductions, such as:
- Medical and dental expenses: Seniors can deduct unreimbursed medical and dental expenses that exceed 7.5% of their adjusted gross income.
- Property taxes and mortgage interest: Seniors who itemize deductions can deduct property taxes and mortgage interest on their primary residence.
- IRA contributions: Seniors can contribute to traditional or Roth IRAs, which may offer tax benefits.
Tax Credits
Seniors may also be eligible for certain tax credits, such as:
- Earned income tax credit (EITC): This credit is available to low- and moderate-income working individuals, including seniors.
- Child tax credit: Seniors who qualify as dependents of a taxpayer may be eligible for the child tax credit.
Resources and Assistance

Seniors may encounter challenges when completing Form 1040-SR. To assist them, various resources are available to provide guidance and support.
These resources include government agencies, tax professionals, and community organizations that offer free or low-cost assistance.
Government Agencies
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS): The IRS provides a wealth of information and resources on Form 1040-SR, including online instructions, publications, and frequently asked questions. Seniors can access these resources by visiting the IRS website or calling the IRS toll-free number at 1-800-829-1040.
- Social Security Administration (SSA): The SSA can provide information on Social Security benefits and how they may affect Form 1040-SR. Seniors can access these resources by visiting the SSA website or calling the SSA toll-free number at 1-800-772-1213.
Tax Professionals
- Enrolled Agents (EAs): EAs are federally licensed tax practitioners who can prepare and file tax returns. They are required to meet continuing education requirements and are subject to a code of ethics. Seniors can find an EA in their area by visiting the National Association of Enrolled Agents website.
- Certified Public Accountants (CPAs): CPAs are state-licensed accountants who can prepare and file tax returns. They are required to meet continuing education requirements and are subject to a code of ethics. Seniors can find a CPA in their area by visiting the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants website.
Community Organizations
- Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA): VITA is a program that provides free tax preparation assistance to low-income taxpayers. VITA sites are typically located at community centers, libraries, and other public locations. Seniors can find a VITA site in their area by visiting the IRS website.
- Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE): TCE is a program that provides free tax counseling and preparation assistance to seniors. TCE sites are typically located at senior centers and other community locations. Seniors can find a TCE site in their area by visiting the IRS website.
FAQ
What are the eligibility criteria for using Form 1040-SR?
To be eligible to use Form 1040-SR, you must be 65 years of age or older by the end of the tax year.
Where can I find Form 1040-SR and its instructions?
You can download Form 1040-SR and its instructions from the IRS website or obtain them by mail by calling 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676).
Can I file Form 1040-SR electronically?
Yes, you can file Form 1040-SR electronically using tax preparation software or through the IRS Free File program.
What is the filing deadline for Form 1040-SR?
The filing deadline for Form 1040-SR is the same as the general tax filing deadline, which is April 15th. However, if you file electronically, you have until October 15th to file.
Where can I get help completing Form 1040-SR?
You can get help completing Form 1040-SR from the IRS website, by calling the IRS at 1-800-829-1040, or by visiting a local IRS office.